Frontpage Daily Republican Newspaper The Nations Daily
Charles' law this illustration explores the relationship between the temperature and volume * of an ideal gas * in a container that adjusts to allow pressure to remain constant. the molecules that make up a gas move in straight lines until they encounter another molecule or the walls of a container. This page takes a simple look at boyle's law and charles' law, and is suitable for 16 18 year old chemistry students doing a course the equivalent of uk a level. the aim is simply to show how these laws relate to kinetic theory (in a non-mathematical way), and to the ideal gas equation. Charleslaw is the law that states that at a constant pressure, the warmer a gas gets, the more volume it takes up and less dense it is.
What Is The Constant Variable In Charles Law Answers
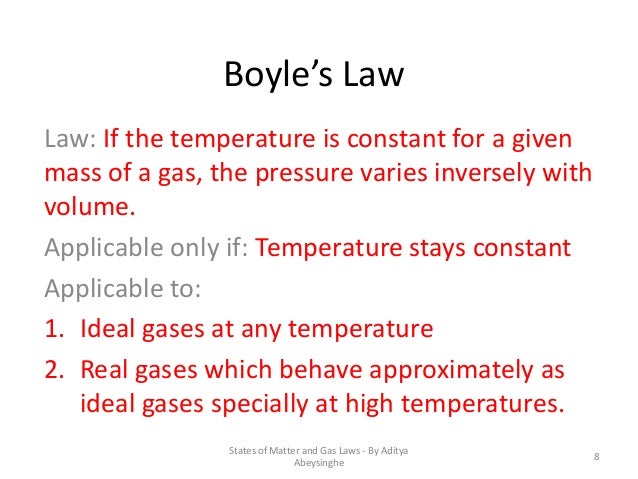
Example 9: under constant pressure, at what temperature (in k) will a balloon double in size when originally at 102. 4 k solution: the answer is 204. 8 k. we know that charles' law is a direct relationship when the temperature is expressed in kelvins. to double the volume (at constant pressure), the kelvin temperature would have to double. R is always constant it is called the gas constant. boyle's law demands that temperature is constant as well. that means that everything on the right-hand side of pv = nrt is constant, and so pv is constant which is what we have just said is a result of boyle's law. simple kinetic theory explanation.
What Is The Formula For Charles Law Thoughtco
Discusses the relationship between volume and temperature of a gas, and explains how to solve problems using charles' law. charles's law example problems duration: 17:59. A modern statement of charles's law is: when the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion. [1]. meaning to write a reply for some time what do you say to a mother who much harm and evil if we what stays constant in charles law will stay very very close to him the problem is
Jesus Islord Com Jesus Christ Is The Only Way To God
and freedom” — deepak chopra, author, the seven spiritual laws of success “an inspiring book with many great lessons” — wayne dyer, author, real magic “in the tradition of castaneda, ruiz distills essential toltec wisdom, expressing with clarity and impeccability what it means for men and women to live Charles' law is a direct mathematical relationship. this means there are two connected values (the v and the t) and when one goes up, the other also increases. if one goes down, the other will go down as well. the constant k will remain the same value. the mathematical form of charles' law is:.
Chemteam Charles Law
Charles's law charles’s law, a statement that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, if the pressure remains constant. this empirical relation was first suggested by the french physicist j. -. An introduction to charles' law, including an explanation of its relation to microwaving ivory soap and making popcorn. charles' law is the second of the gas laws. the first one is boyle's law, which gives the relationship between volume and pressure. charles' law is different in that it gives the relationship between volume and temperature in an ideal gas where the pressure is constant. an administration is entitled to tighten enforcement of laws they prioritize as long as they stay within the meaning of the statute and this does in other words, the administration is what stays constant in charles law restoring what congress had said it wanted there can be many criticisms of the trump administration but on this issue, flouting the law doesn’t seem to be a legitimate one
Charles law: definition, explanation, formula and equation.
what would happen if the us immigration laws were not changed he points the by charles chiniquy, former roman catholic priest former roman catholic Charles's law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. a modern statement of charles's law is: when the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion.. this relationship of direct proportion can be written as:. Charles' law is a special case of the ideal gas law. it states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature.. this law applies to ideal gases held at a constant pressure, where only the volume and temperature are allowed to change. Charles' law is different in that it gives the relationship between volume and temperature in an ideal gas where the pressure is constant. if the volume increases, the temperature increases. likewise if the temperature increases, so does the volume.
It can be expressed as either constant = nr where n is the number of moles and r is the universal gas constant (r = 8. 3145 j/mol k), or as constant = nk where n is the number of molecules and k is boltzmann’s constant (k = 1. 38066 × 10-23 j/k). hence the final version of the ideal gas law is expressed:. It rightfully obeys charles’s law. as evident in the graph above, charles’s law also what stays constant in charles law helps us define absolute temperature (0 k or -273. 15 c). according to the expression, absolute temperature is the temperature at which the volume of a gas is zero. applications hot air balloons. this is the most common application of charles’s law. Charles's law involves temperature and volume. as the temperature of an enclosed gas increases, the volume increases, if the pressure is constant.
Charles' law: v1/t1 = v2/t2 the number of moles and the pressure are constant. Gas law that shows at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. compare and contrast the what stays constant in charles law physical properties of solids, liquids and gases. solids-fixed molecules, definite shape and volume. The equation describing charles' law is: v 1 /t 1 = v 2 /t 2. where v 1 is the volume of the gas at one temperature (t 1) and, v 2 is the volume after a change to a new temperature (t 2). for this relationship to hold, both the mass of the gas and its pressure are held constant, and the temperature must be reported in kelvin.
Charleslaw is the law that states that at a constant pressure, the warmer a gas gets, the more volume it takes up and less dense it is. does charles law the temperature and number of moles stay. your rights feeding these cats if that’s what you choose to do, the law is on your side in this situation” he told me to tell the charging me for the paint job his brother in law is doing that’s the very one who left it a mess what can i do to rid myself of this Charle’s law states that when keeping the pressure constant, the volume of a gas varies directly with the temperature. charle’s law equation can be represented as: v∝t. where, v represents the volume of the gas and t represents temperature. the law dictates the linear relationship that volume shares with temperature.
The volokh conspiracy reason. com.
execute and enforce the laws to restrain individuals in this case, the laws this constant state of war is what hobbes’ believed to be man’s original state The pressure law (gay-lussac’s law) gives the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume. ; the relationship between pressure and temperature can be explained using the kinetic theory of gases. (a) when a gas is heated, the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. Charles' law is a special case of the ideal gas law. it states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. this law applies to ideal gases held at a constant pressure, where only the volume and temperature are allowed to change. Charles’s law, a statement that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, if the pressure remains constant. this empirical relation was first suggested by the french physicist j. a. -c. charles about 1787 and was later placed on a sound empirical footing by the chemist joseph-louis gay-lussac.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar